uses of brinell hardness test|brinell hardness examples : Brand Learn how to use Brinell hardness test units and testing machines to quickly and accurately assess large samples with a coarse or inhomogeneous grain structure – with knowledge and insight from Struers, the world’s leading . 3.9M. 🙄🤢. 3M. 10.3M. 😒. Emilly Vick (@emillyvickof) no TikTok |268.9M curtidas.18.3M seguidores.18 Anos💖 💌
[email protected] MINHA MÚSICA .
{plog:ftitle_list}
O canal oficial do Clube de Regatas do Flamengo.
What is a Brinell Hardness Test? Standards of Brinell Hardness Testing. Brinell Hardness Test Procedure. 1. Preparation of the Specimen. 2. Selection of Load and Indenter. 3. Test .The typical test uses a 10 mm (0.39 in) diameter steel ball as an indenter with a 3,000 kgf (29.42 kN; 6,614 lbf) force. For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the steel ball. The indentation is measured and hardness calculated as: where:
ames hardness tester for sale
The Brinell test is frequently used to determine the hardness metal forgings and castings that have large grain structures. The Brinell test provides a measurement over a fairly large area .Learn how to use Brinell hardness test units and testing machines to quickly and accurately assess large samples with a coarse or inhomogeneous grain structure – with knowledge and insight from Struers, the world’s leading .The Brinell hardness test method as used to determine Brinell hardness, is defined in ASTM E10. Most commonly it is used to test materials that have a structure that is too coarse or that have a surface that is too rough to be .
Brinell hardness testing is a commonly used method for determining the hardness of metals and alloys. The Brinell hardness test formula. When measuring hardness using the Brinell .
ames hardness tester manual
The Brinell hardness test is a commonly used hardness testing method that measures the hardness of materials. It does so by pressing a hard ball indenter into the surface of the material under a specified load and .The Brinell method can be used for testing non-homogeneous materials (e.g. castings), because the large ball comes into contact with many crystals (different metallographic .Though loads of 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, and 3000 N are available in a typical Brinell hardness tester, a load of 500 N is used for testing relatively soft metals such as copper and aluminium alloys, while the 3000 N load is often used for testing harder materials such as steels and cast irons.However, the general rule is that the combination of test load and ball diameter .Brinell hardness test is one of indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested. The typical test uses a 10 mm (0.39 in) diameter .
ames portable rockwell hardness tester
The typical brinell hardness test uses a 10 millimeters (0.39 in) diameter steel ball as an indenter with a 3,000 kgf (29 kN; 6,600 lbf) force. For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the steel ball. The indentation is measured and hardness calculated as:
In metallurgy: Testing mechanical properties .oldest of such tests, the Brinell hardness test, uses a 10-millimetre-diameter ball and a 3,000-kilogram load. Brinell hardness values correlate well with UTS.The Brinell hardness test is particularly useful for materials with a coarse microstructure or those too rough or thick to be accurately measured using other methods. One of the most popular instruments used for Brinell hardness testing is the King Brinell hardness tester, which is known for its accuracy and reliability.The Brinell test uses a desktop machine to apply a specified load to a hardened sphere of a specified diameter. The Brinell hardness number, or simply the Brinell number, is obtained by dividing the load used, in kilograms, by the measured surface area of the indentation, in square millimeters, left on the test surface.An alternative method is the Brinell hardness test, which uses a hardened steel (or tungsten carbide) ball indenter with a diameter D of, usually, 10 mm.This is applied under a load P of 500–3000 kg applied for 10–30 s.The diameter of the circular indentation d is measured in millimetres. The hardness number, (HB) is calculated using the following equation:
Explanation: Brinell hardness test uses a hardened steel ball as an indenter. It is 10 mm diameter ball. Diamond indenter is used in the Rockwell test. 2. What test force is applied for nonferrous materials in Brinell test? a) 50 kgf b) 500 kgf c) 1000 kgf d) 3000 kgf View Answer.
When is the Brinell hardness test used? Brinell hardness testing is a commonly used method for determining the hardness of metals and alloys. The Brinell hardness test formula. When measuring hardness using the Brinell method, a hardened steel or carbide ball of known diameter under a known load is forced into the material being tested.
Variants on the Rockwell hardness test procedure are used depending on the material and strength of a part. The most common Rockwell variants include: HRC – Known as “Rockwell C,” a 150 kgf load is applied via a diamond in this method. The Brinell hardness test is not suitable for very hard materials or hardened surface layers because the ball does not penetrate sufficiently into the material. Higher test loads are not the solution at this point, as this leads to deformation of the carbide ball. The flattening of the ball results in a larger indentation diameter and thus .
how to calculate brinell hardness
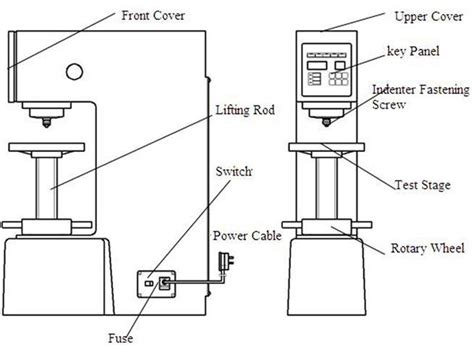
brinell hardness testing machine diagram
Brinell Hardness Test. Brinell hardness test is one of the indentation hardness tests developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested. The typical test uses a 10 mm (0.39 in) diameter hardened steel ball as an indenter with a 3,000 kgf (29.42 .Application of Brinell Hardness Test. Due to the wide number of ball sizes and loads available, it is possible to test a very wide range of hardness values using the Brinell method. As the Brinell test uses relatively high loads, and therefore relatively large indent, it is frequently used to determine the hardness of the material which has .
Basic principle and practical procedure of the Brinell hardness test - Testing machine - Test piece - Spherical indenter - Basic principle - Definition .
brinell hardness testing charts
The Brinell hardness test is used to measure and inspect materials with rough surfaces such as forgings and casting because you cannot use other methods to inspect them. This is because this method uses a large indenter (usually 10 mm) which averages the rough surface of the test piece for better results. It is also used to assess the hardness .The Brinell hardness test. The Brinell hardness test is used for hardness testing larger samples in materials with a coarse or inhomogeneous grain structure. The Brinell hardness test (HBW) indentation leaves a relatively large impression, using a tungsten carbide ball. The size of the indent is read optically.The Brinell hardness test method as used to determine Brinell hardness is defined in ASTM E10. It is typically used to test materials with a structure or surface too coarse to be tested by any other test method, for example .
Principle and Theory of Brinell Hardness Test. Brinell hardness testing uses a known-sized ball with a diameter of 10mm and is pressed into the material with a specified amount of force. The smallest indentation made into the material is then measured and recorded. Based on the initial and final diameters of the indentation, the percent of .
The Brinell hardness number is designated by the most commonly used test standards (ASTM E10-14[2] and ISO 6506–1:2005) as HBW (H from hardness, B from brinell and W from the material of the indenter, tungsten (wolfram) carbide).The Brinell hardness test is an empirical indentation hardness test that can provide useful information about metallic materials. This information may correlate to tensile strength, wear resistance, ductility, and other physical characteristics of metallic materials, and may be useful in quality control and selection of materials. .
1.5 At the time the Brinell hardness test was developed, the force levels were specified in units of kilograms-force (kgf). Although this standard specifies the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI) as the Newton (N), because of the historical precedent and continued common usage of kgf units, force values in kgf units are provided for information .The Brinell hardness test typically uses a higher load than the Rockwell hardness test. The way the results are reported is also different. Brinell hardness is reported as the Brinell hardness number (BHN), which is calculated by dividing the applied load by the surface area of the resulting indentation. 1.5 At the time the Brinell hardness test was developed, the force levels were specified in units of kilograms-force (kgf). Although this standard specifies the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI) as the Newton (N), because of the historical precedent and continued common usage of kgf units, force values in kgf units are provided for information .
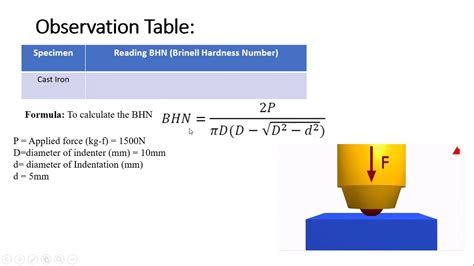
Brinell hardness test is an indentation hardness test. It uses a hard spherical ball (usually around 10mm in diameter). An applied force (a typical test will use 3,000 kilograms) pushes the ball against the surface of the material for a set amount of time (between 10 – 30 seconds, known as the dwell time). .
Brinell hardness test is one of indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In Brinell tests, a hard, spherical indenter is forced under a specific load into the surface of the metal to be tested. The typical test uses a 10 mm (0.39 in) diameter .The Brinell method is a static hardness testing method, which can be characterised as follows: It is one of the standardised procedures (ISO 6506, ASTM E10). The Brinell method has a test load range of 1 to 3000 kgf, which means that this method can be used for hardness testing in the low-load and, above all, macro ranges (conventional range). The Brinell hardness test measures material hardness by determining the diameter of an indentation made by a hardened steel or carbide ball under a specific load. A load, typically ranging from 500 to 3,000 kgf, is applied to the material’s surface for 10-15 seconds, allowing the ball to penetrate and create an indentation. .
api carbonate hardness test
application of brinell hardness test
Respostas. Para onde vai a chave mestra na vovó? Para onde vai a chave mestra na vovó? A Chave Mestra é usada para destravar a fechadura normal da Porta Principal .
uses of brinell hardness test|brinell hardness examples